Spanish verb conjugation: AR, ER, and IR ending verbs
Anyone who's spent time learning Spanish knows the moment when a simple sentence becomes a mental puzzle. Unlike English, where verbs largely stay the same regardless of who's performing the action, Spanish transforms its verbs dramatically based on the subject, tense, and voice.
In English, verbs barely change:
- I talk
- You talk
- They talk
But in Spanish?
- Yo hablo
- Tú hablas
- Ellos hablan
Each subject changes the verb. This might feel tricky at first - but it’s exactly what gives Spanish its flow and precision.
This guide breaks down how to conjugate the three main types of regular Spanish verbs (-ar, -er, and -ir) in common tenses, complete with clear charts, practical tips, and real-world examples.
How to conjugate Spanish verbs step-by-step
All Spanish verbs end in -ar, -er, or -ir in their base form (called the infinitive), like:
A Spanish verb has two parts:
- The stem - what remains after removing the -ar, -er, or -ir ending
- The ending - the part that changes based on who's performing the action and when
For example, with "hablar" (to speak):
- The stem is "habl-"
- The ending "-ar" gets replaced with a new ending during conjugation
Spanish subject pronouns for verb conjugation:
- Yo - I
- Tú - You (informal)
- Usted - You (formal)
- Él/Ella - He/She
- Nosotros/as - We
- Vosotros/as - You all (Spain)
- Ustedes - You all (Latin America)
- Ellos/Ellas - They
Because the verb ending makes it clear who's performing the action, Spanish often drops the subject:
"Hablo español" = "I speak Spanish" (no need to say "Yo").
Spanish regular verbs conjugation: Patterns
Regular verbs follow predictable patterns based on their infinitive endings, making them the perfect starting point for mastering Spanish conjugation.
The basic rule for conjugating regular verbs in most tenses is straightforward:
- Remove the infinitive ending (-ar, -er, -ir)
- Add the appropriate ending for the subject and tense
Let's explore how this works across the three most essential tenses for beginners.
Present tense conjugation for AR, ER, and IR verbs
The present tense in Spanish is versatile, covering multiple English constructions:
- I speak
- I am speaking
- I do speak
To form the present tense, drop the infinitive ending and add the specific endings for each subject.
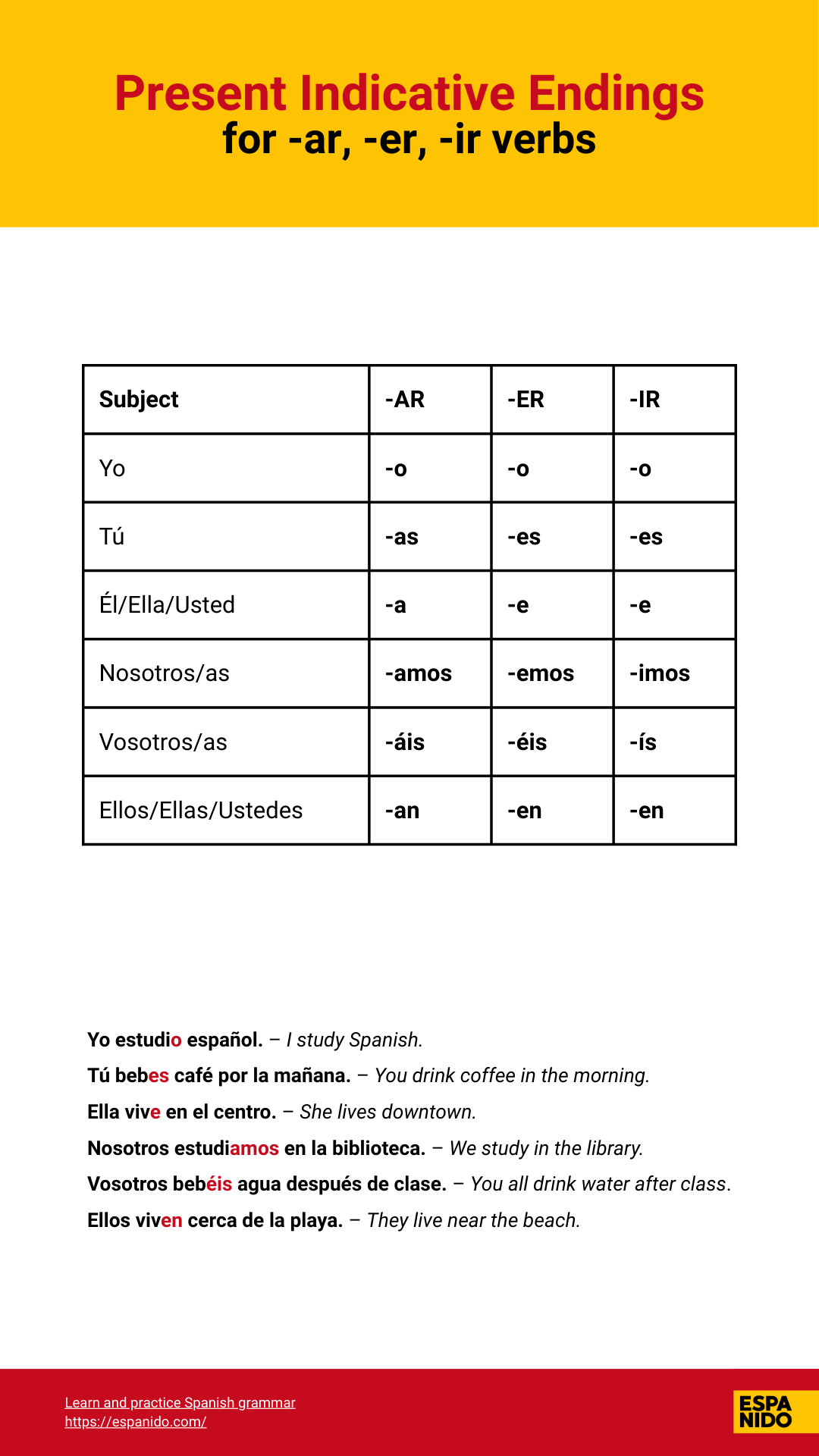
Present tense endings for conjugating AR, ER, and IR verbs
- AR:
yo -o, tú -as, él/ella -a, nosotros -amos, vosotros -áis, ellos -an
- ER:
yo -o, tú -es, él/ella -e, nosotros -emos, vosotros -éis, ellos -en
- IR:
yo -o, tú -es, él/ella -e, nosotros -imos, vosotros -ís, ellos -en
Conjugation chart for AR, ER, and IR Verbs in Present tense
Examples of conjugating AR, ER, and IR verbs in Present Tense
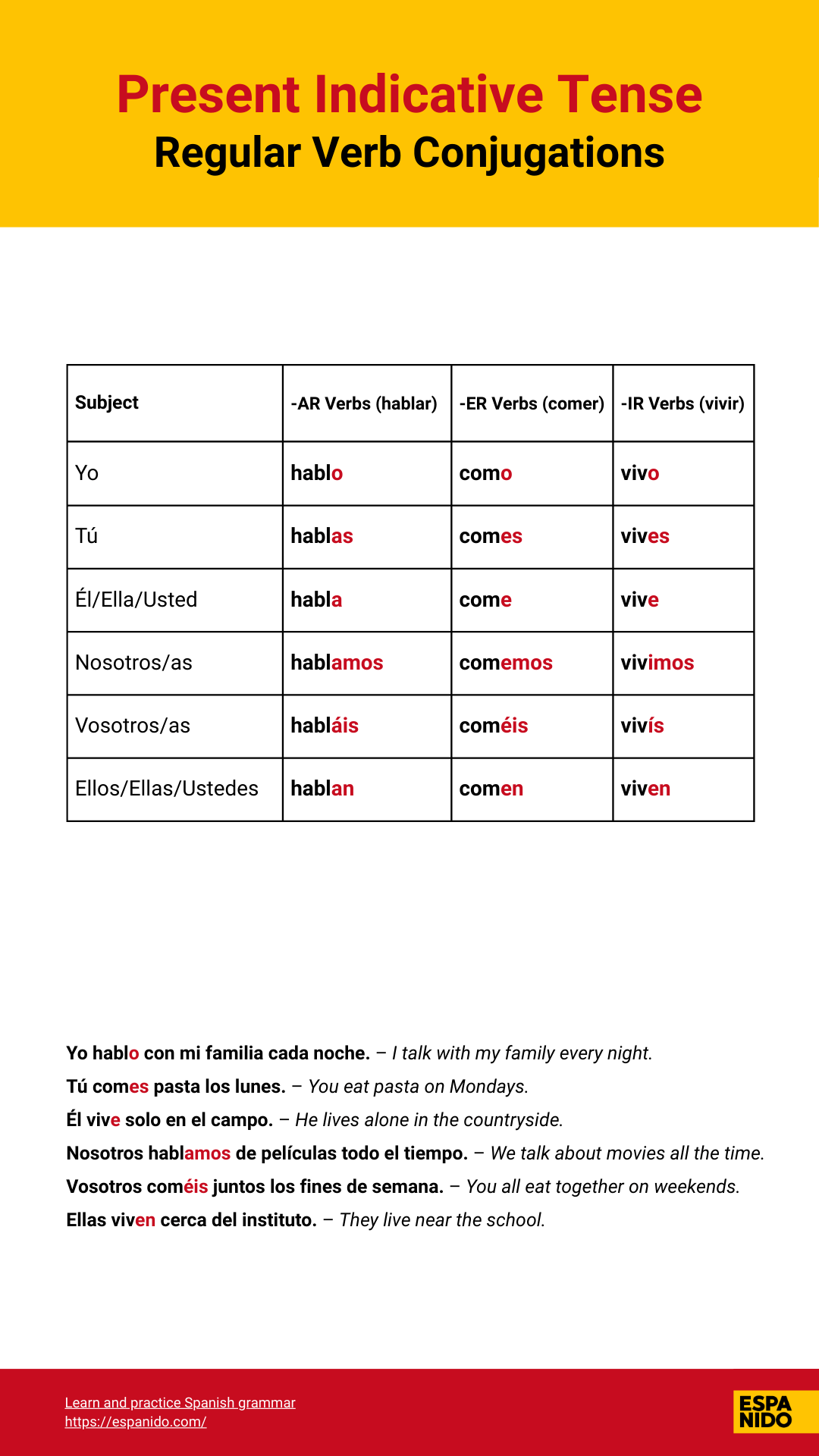
AR verb (hablar):
- Yo hablo
- Tú hablas
- Él/Ella/Usted habla
- Nosotros/as hablamos
- Vosotros/as habláis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablan
ER verb (comer):
- Yo como
- Tú comes
- Él/Ella/Usted come
- Nosotros/as comemos
- Vosotros/as coméis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes comen
IR verb (vivir):
- Yo vivo
- Tú vives
- Él/Ella/Usted vive
- Nosotros/as vivimos
- Vosotros/as vivís
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes viven
Note: -ER and -IR verbs are nearly identical in the present tense, except for the "we" and "you all" forms.
Practice the present tense (Presente de Indicativo) with interactive exercises.
Conjugation chart for regular verbs Hablar, Comer, and Vivir
Test your knowledge of AR verbs by practicing the conjugation of caminar.
How to conjugate Spanish verbs in Past tense (Preterite)
The preterite tense describes completed actions at a specific point in the past.
The conjugation rule remains consistent:
- Remove the infinitive ending (-ar, -er, -ir)
- Add the appropriate ending for the subject and tense
However, the regular preterite has two sets of endings: one for -ar verbs and another shared by both -er and -ir verbs.
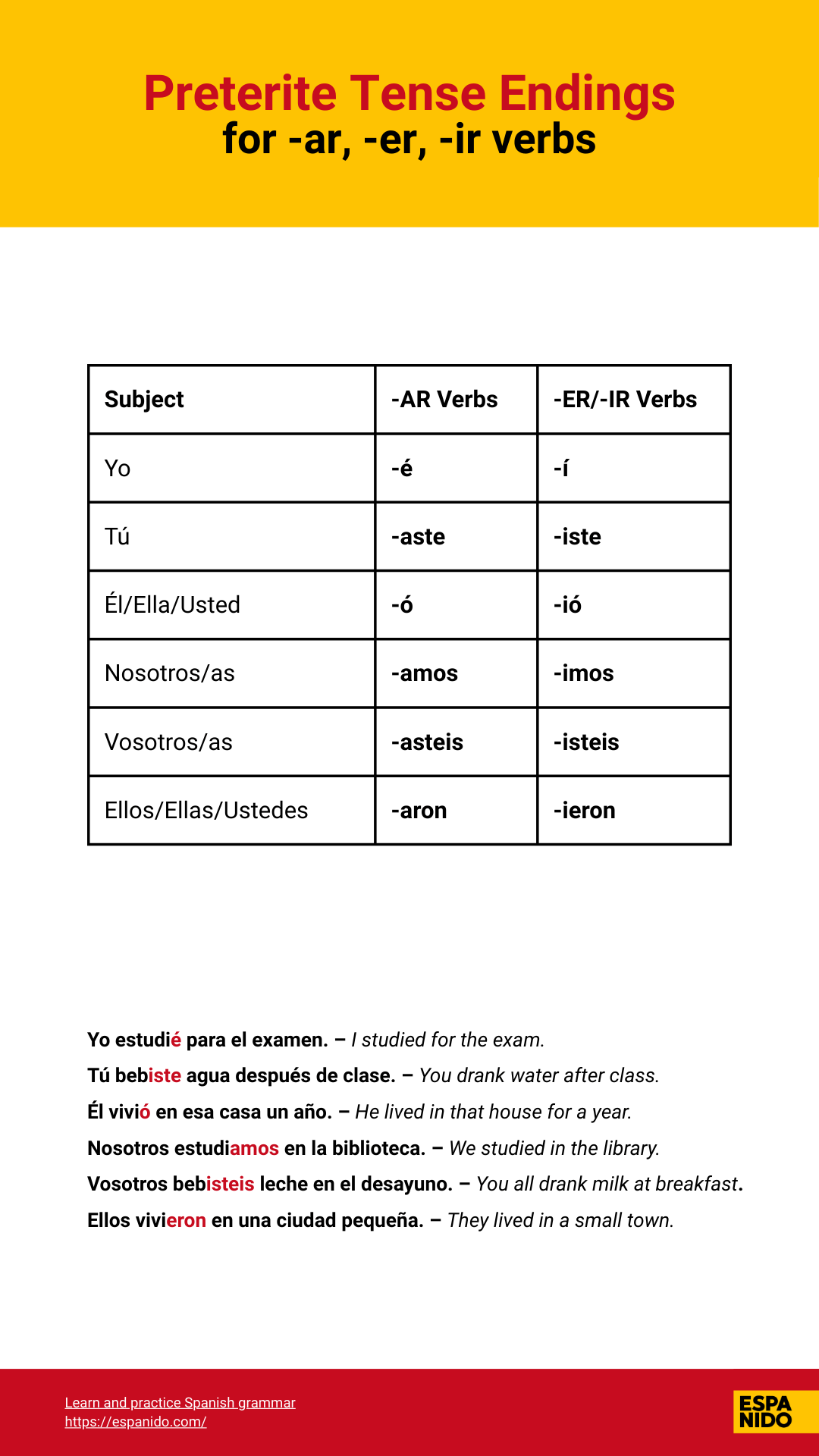
Conjugation endings for regular verbs in Preterite
- AR:
yo -é, tú -aste, él/ella -ó, nosotros -amos, vosotros -asteis, ellos -aron
- ER / -IR:
yo -í, tú -iste, él/ella -ió, nosotros -imos, vosotros -isteis, ellos -ieron
Conjugation Chart for AR, ER, IR Verbs in Preterite
Examples of conjugating AR, ER, and IR verbs in Past Tense
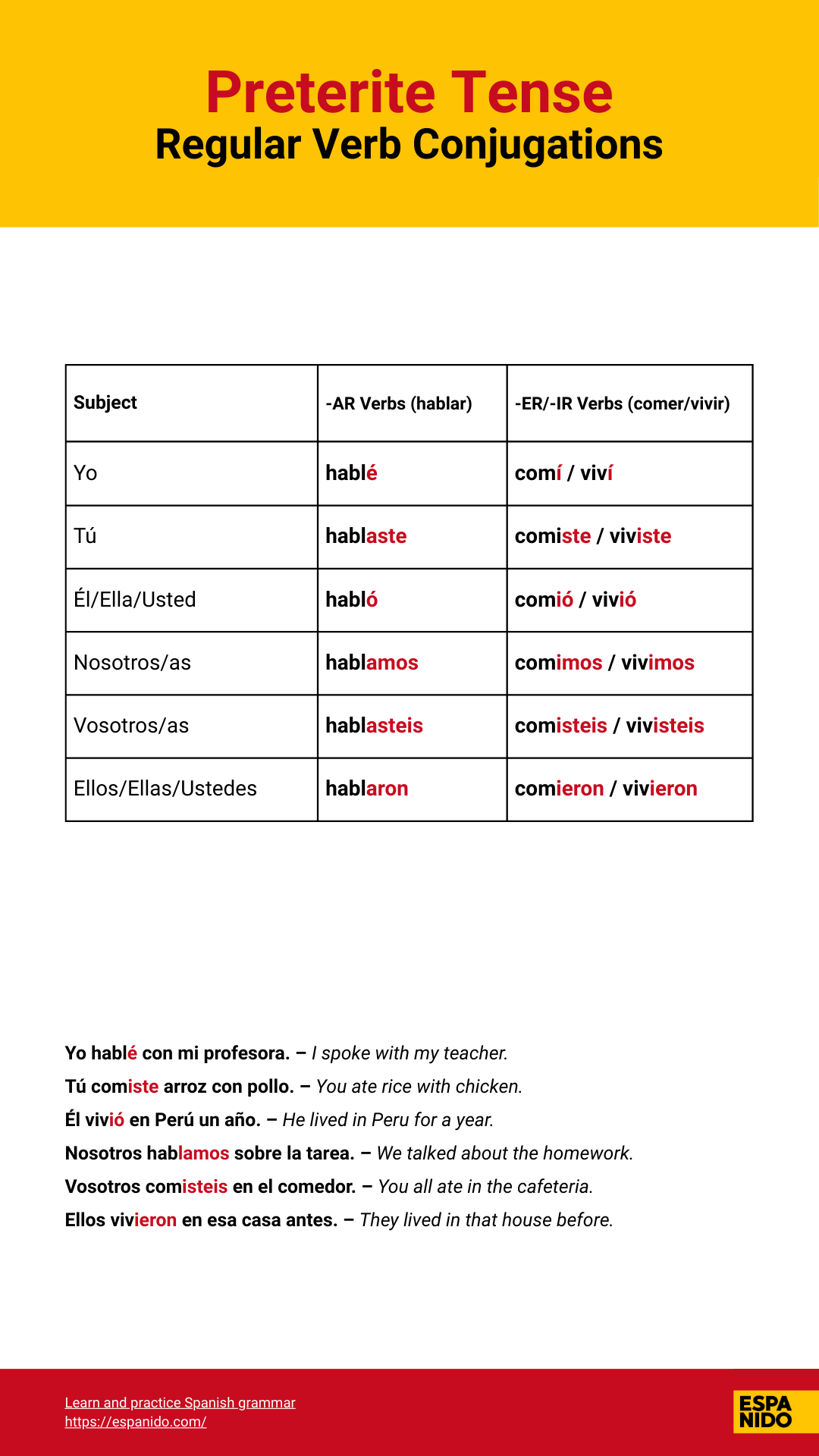
AR verb (hablar):
- Yo hablé
- Tú hablaste
- Él/Ella/Usted habló
- Nosotros/as hablamos
- Vosotros/as hablasteis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablaron
- Yo comí / viví
- Tú comiste / viviste
- Él/Ella/Usted comió / vivió
- Nosotros/as comimos / vivimos
- Vosotros/as comisteis / vivisteis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes comieron / vivieron
Conjugation chart for regular verbs Hablar, Comer, and Vivir in Preterite
Practice the preterite tense (Pretérito Indefinido) with interactive exercises.
Expert Tip: Keep an eye on the accent marks! The tildes (written accents) on the final vowel of the yo (-é, -í) and él/ella/usted (-ó, -ió) forms in the preterite are crucial. They can change both the tense and subject of a sentence. Compare:
- mando (I command)
- mandó (he/she/you commanded)
Practical Advice:
The nosotros form (we) of -ar verbs is the same in both present and past: -amos.
So a sentence like “Cocinamos paella” can mean:
→ “We cook paella” (present)
→ or “We cooked paella” (past)
How do you know the difference? Look at the context - words like “ayer” (yesterday) or “siempre” (always) will help you to clarify which tense is being used.
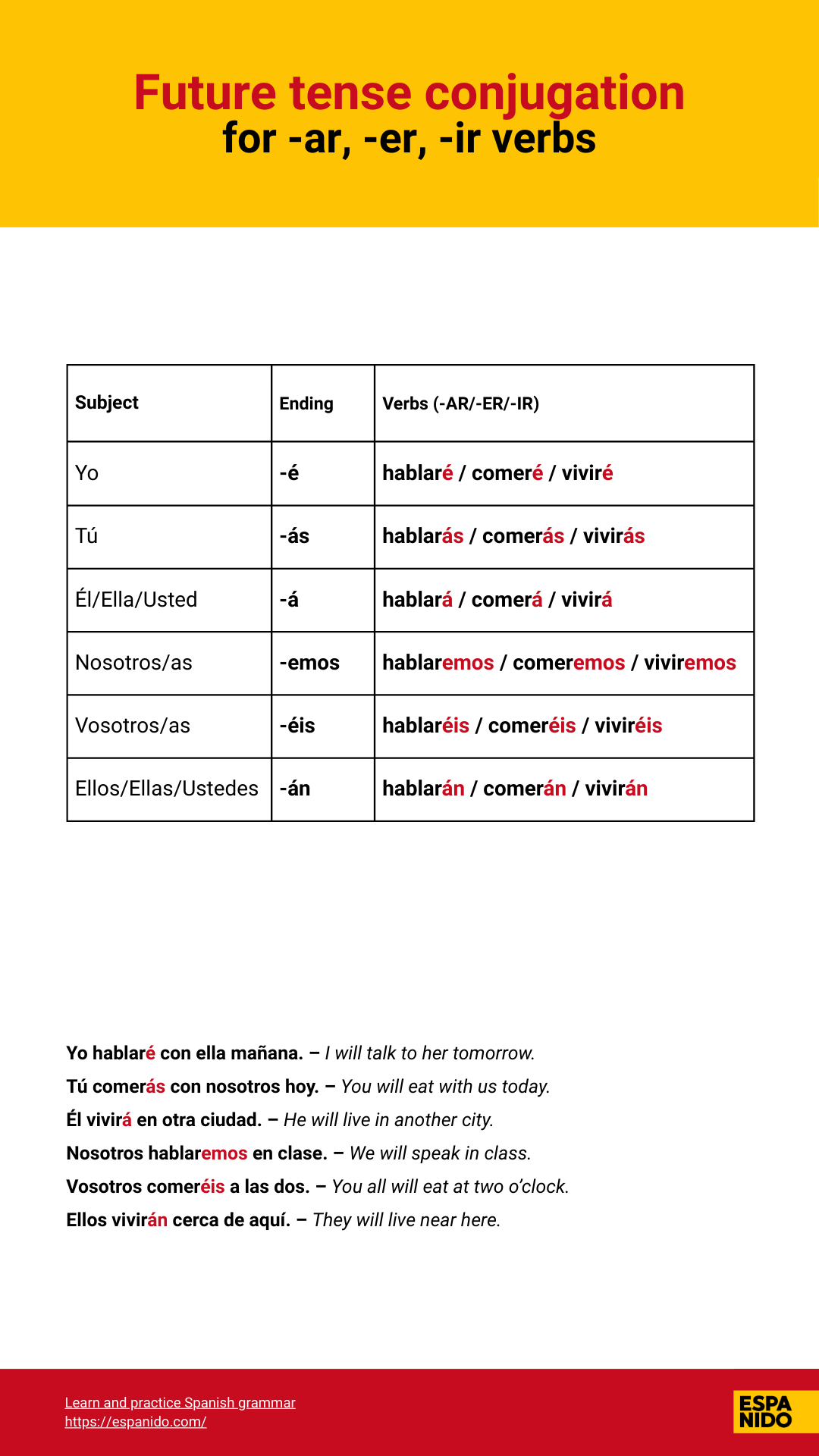
Future tense conjugation for AR, ER, and IR verbs
The future tense works differently from the present and preterite. Instead of removing the infinitive ending, you
- keep the entire infinitive
- add the future tense endings directly to it
Works the same for -ar, -er, and -ir verbs.
Future tense endings for regular Spanish verbs
yo -é, tú -ás, él/ella -á, nosotros -emos, vosotros -éis, ellos -án
Examples (hablar / comer / vivir):
- Yo hablaré / comeré / viviré
- Tú hablarás / comerás / vivirás
- Él/Ella/Usted hablará / comerá / vivirá
- Nosotros/as hablaremos / comeremos / viviremos
- Vosotros/as hablaréis / comeréis / viviréis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hablarán / comerán / vivirán
Conjugation chart for AR, ER, and IR Verbs in Future tense
Patterns in ER and IR verbs you should know
- ER and -IR verbs share endings in the preterite and future
- In the present, they differ only for nosotros and vosotros:
- ER: emos / éis
- IR: imos / ís
Er and IR verbs follow almost the same pattern, so if you know one, the other is easy to pick up.
Irregular verbs conjugation in Spanish
While regular verbs follow clear patterns, many common Spanish verbs are irregular - they don’t follow the usual rules. These irregular verbs often fall into a few main groups.
- Spelling changes (to preserve pronunciation)
- Stem changes (e.g., e → ie, o → ue)
- Totally irregular forms (like ser, ir, tener)
Tip: Focus on regular verbs first-they’re your best entry point. Once you're comfortable, you can explore all the verb rules and practice conjugating them here.
Reflexive verbs and Present Progressive in Spanish
Once you’ve got the main tenses down, there are other useful verb forms to learn:
- Present Progressive Used to talk about what’s happening right now. Formed with a conjugated form of "estar" plus the gerund (-ando for -ar verbs, -iendo for -er/-ir verbs) 👉 Estoy hablando = I am speaking
- Reflexive verbs These show that someone is doing something to themselves. Use reflexive pronouns (me, te, se, nos, os, se) before the conjugated verb 👉 Me lavo las manos = I wash my hands See how reflexive verbs work and practice here
Tips and best practices for learning Spanish conjugation
Conjugation might feel tricky at first, but with the right habits, it gets easier. Try these:
- Use verb charts as a guide while you're still getting used to the endings.
- Listen to Spanish music - repeated lyrics help you remember forms without even trying.
- Watch Spanish movies or shows with subtitles to hear how verbs are used in context.
- Build full sentences on Espanido - this helps you use verbs, not just memorize them.
- Practice speaking on Tandem or HelloTalk, or get feedback from a tutor on Italki - real conversation makes it stick.
Your journey to Spanish fluency
Learning regular -ar, -er, and -ir conjugations is a major step to Spanish fluency. These are the verbs that carry conversations across tenses.
Practice Spanish conjugation every day. Use the tools, lean on the patterns, and don’t fear mistakes. Everyone starts at step one.
¡Buena suerte en tu viaje con el español! (Good luck on your journey with Spanish!)